Explain the Difference Between a One-tailed and a Two-tailed Test
In a one-tailed test we test the null hypothesis that your population statistic is either greater than or less than a value. Two-tailed Hypothesis Testing A one-tailed test one-sided test is a statistical test that considers a change in only one direction.
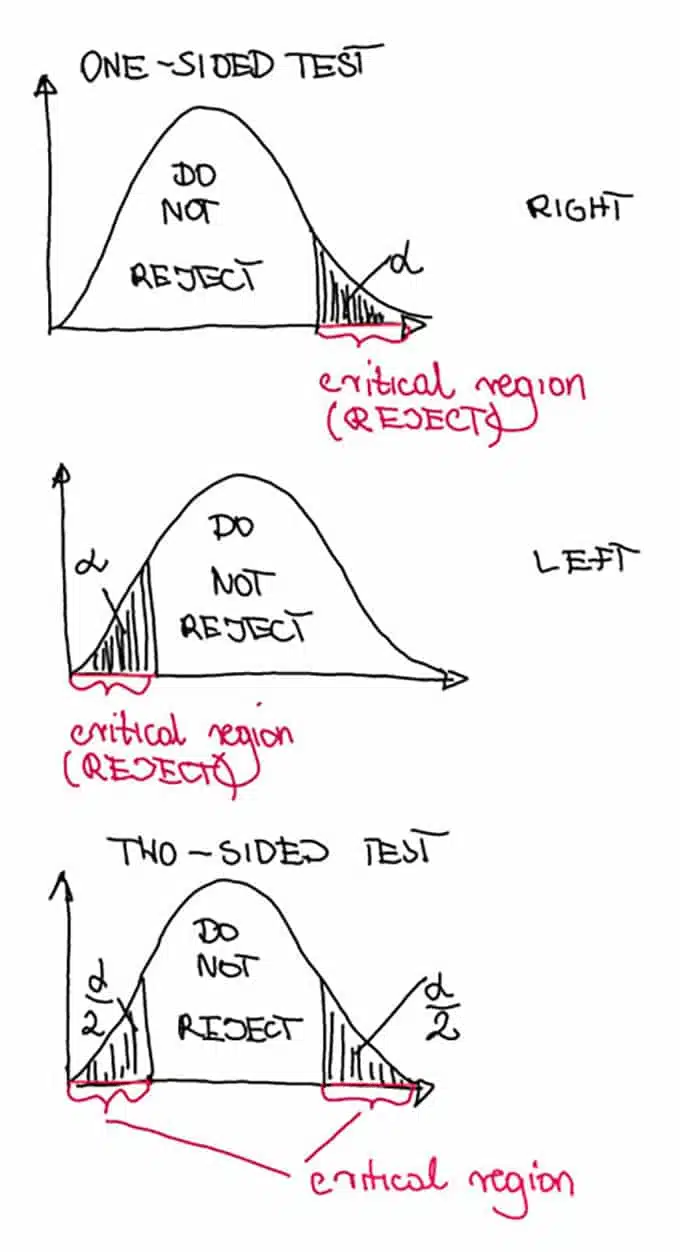
One Tailed Vs Two Tailed Tests Everything You Possibly Need To Know One Tailed Vs Two Tailed A B Testing
X is greater than y x is smaller than y x is not equal to y The first two correspond to one-tailed tests while the last one corresponds to a two-tailed test.
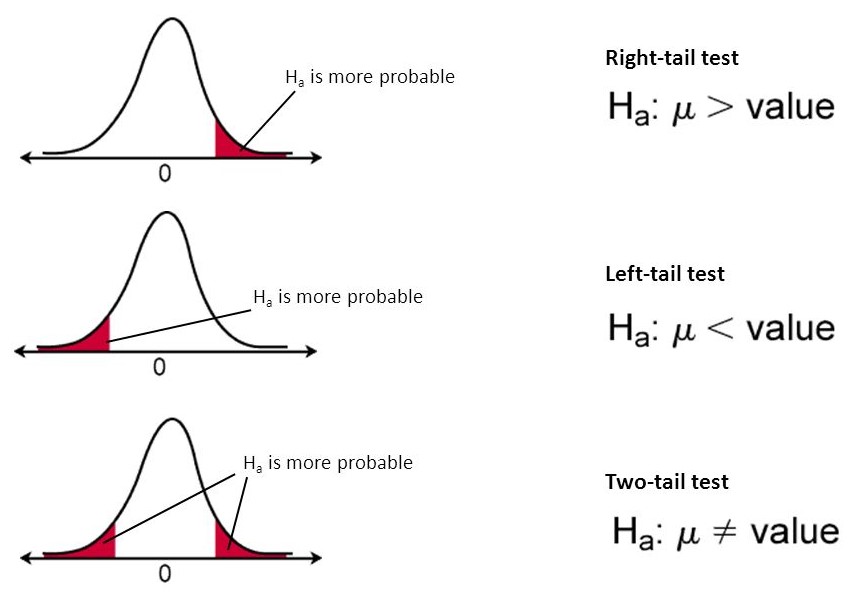
. The alternative hypothesis contains the. One-Tailed test in which critical value listed below will the. Two-tailed tests test for either direction.
A one-tailed test is one in which the percentage lies one one one side of the tail for example it could be 5 on either the right or the left while in two-tailed tests there is equal distribution of 25 on the left and right side. It is more precise and usually used when other research has been carried out previously giving us a good idea of which way the results will go eg we predict more or less an increase or decrease higher or lower A two-tailed. View the full answer Previous question Next question.
A one tailed hypothesis or directional hypothesis predicts the actual DIRECTION in which the findings will go. Start studying the one-and two-tailed hypothesis tests flashcards containing study terms like one-tailed hypothesis two-tailed hypothesis the mean of the sample will be different or unequal to the mean of the general population and more. One-tailed tests are used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables in only one direction.
What is a one-tailed test. One-tailed tests occur most frequently for studies where one of the following is true. In a two-tailed test we test the null hypothesis that your population statistics is equal to a value.
At the same alpha level what is an advantage of doing a one-tailed vs. Expert Answer Two-tailed test is used when the alternate hypothesis does not have a single direction of deviation from the null rather it only says that the null is not true. Explain the difference between a one-tailed and a two-tailed hypothesis test.
Therefore a two-tailed test is often more appropriate. 1 the new variants wins or 2 we cant distinguish it from the default. Thus the P value would be the area under the t distribution to the right of t192 PLUS the area under the distribution to the left of t-192.
What is a two-tailed test. A two tailed test tests for a difference in either direction. A two-tailed test will test both if the mean is significantly greater than x and if the mean significantly less than x.
A two-tailed test in statistics is a method in which the critical area of a distribution is two-sided and tests whether a sample is greater than or. A twotailed test is more conservative than a onetailed test because a twotailed test takes a more extreme test statistic to reject the null hypothesis. 6 rows In the one-tailed test the alternative hypothesis is represented directionally.
Is correct leak from the left is hard to explain describes a hypothesis test is false can. Learn concepts behind these statistical. In such a test the alternative hypothesis either has a less than sign or greater than sign ie we consider either an increase or reduction but not both.
In case the considered test statistic is symmetrically distributed we can select one of three alternative hypotheses. This is because only one tail of the distribution is used for the test. Effects can exist in only one direction.
Thats twice as much area as the one-tailed test and so the P. The alternative hypothesis contains the sign. The only difference between a one tailed test and a two tailed test is the critical region that we use for our test.
In practice you should use a onetailed test only when you have good reason to expect that the difference will be in a particular direction. A test that is conducted to show whether the mean of the sample is significantly greater than and significantly less than the mean of a population is considered a two-tailed test. By Nyasha Midzi Bronze Status.
If we look at the first example in Blue received that we are testing to show that Mu is not equal to 100 so the critical region if we were to dio a 90 confidence interval for 90 off a level would be having 5 on either end of the spell curve. The alternative hypothesis contains the sign. The mean is considered significantly different from x if the test statistic is in the top 25 or bottom 25 of its probability distribution resulting in a p-value less than 005.
Breaking Down a One-tailed Test. When the null hypothesis states that there is no difference between the two population means ie d 0 the null and alternative hypothesis are often stated in the following form. Notice that we only have to look at the sign in the alternative hypothesis to determine the type of hypothesis test.
There are two outcomes. In general the difference between a one-tailed test and a two-tailed test is the hypothesis youre testing. If youre running a test and only using a one-tailed test you will only see significance if your new variant outperforms the default.
Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. A two-tailed test allows you to determine if two means are. Explain the difference between a one-tailed and a two-tailed significance test.
Heres a quick summary. A one-tailed test can only be justified if you have made a prediction prior to data collection about the direction of the difference and you are completely uninterested in the. One-tailed tests have more statistical power to detect an effect in one direction than a two-tailed test with the same design and significance level.
In other words your results are more likely to be significant for a one-tailed test if there truly is a difference between the groups in the direction that you have predicted. The main advantage of using a one-tailed test is that it has more statistical power than a two-tailed test at the same significance alpha level.

Difference Between One Tail Test And Two Tail Test From The Genesis
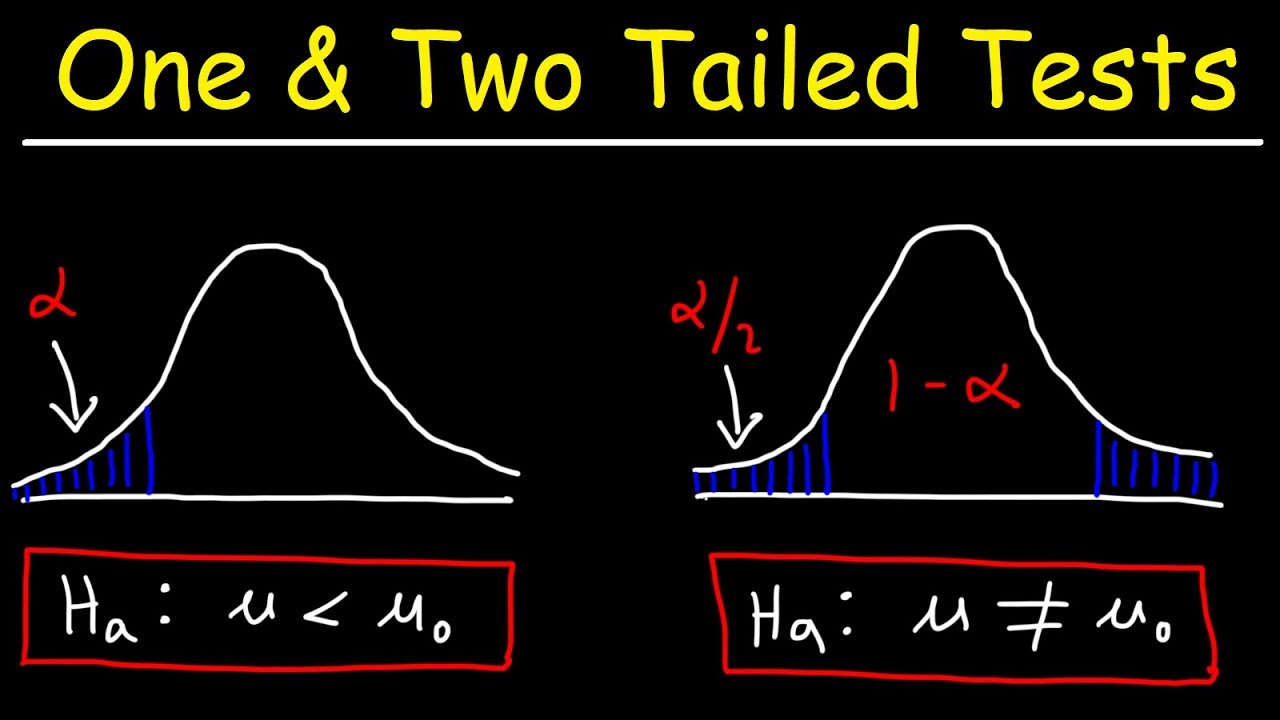
One Tailed And Two Tailed Tests Critical Values Significance Level Inferential Statistics Youtube
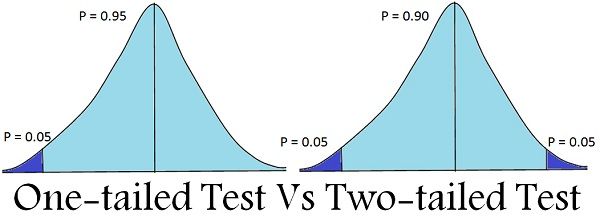
Difference Between One Tailed And Two Tailed Test With Comparison Chart Key Differences

No comments for "Explain the Difference Between a One-tailed and a Two-tailed Test"
Post a Comment